Describe the Structure of the Spinal Cord.
The interior of the cord is formed by gray matter which is surrounded bywhite matter Figure 111A. Anatomically the spinal cord is made up is made up of nervous tissue and is integrated into the spinal column of the backbone.
10 Surprising Facts About The Spinal Cord Sapna Pain Management Blog
The spinal cord is a cylindrical structure lying in the neural canal of the vertebral column.
. Of Biology Class 10th. The posterior-most region of the spinal cord tapers into a thin fibrous thread-like structure called Filum terminate. Humans have a total of 31 segments.
Its diameter varies at different levels being enlarged in the cervical and lumbar regions. It is also covered by meninges. The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system CNS which extends caudally and is protected by the bony structures of the vertebral column.
In fact it is the most important structure for any vertebrates. Spinal cord has the following functions. Get FREE solutions to all questions from chapter COORDINATION - THE LINKING SYSTEM.
SPINAL CORD The main pathway for information connecting the brain and peripheral nervous system. With the help of a suitable diagram describe the structure and function of a neuron. In transversesections the gray matter is conventionally divided into dorsalposterior lateraland ventralanterior horns.
Spinal Cord Structure The spinal cord is a thick long fragile and whitish cord of nerve tissue that starts at the end of the brainstem and extends through the spinal column. Like the vertebral column the spinal cord is divided into segments. The spinal cord is a part of the central nervous system.
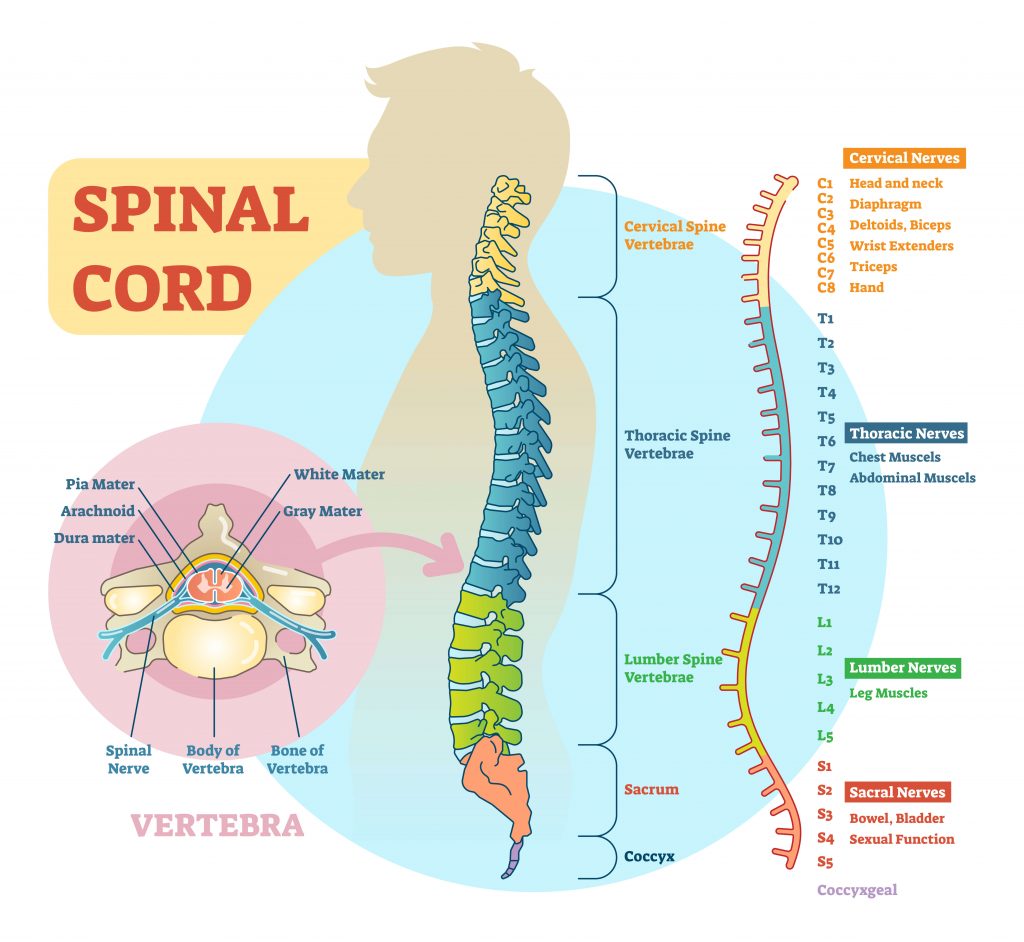
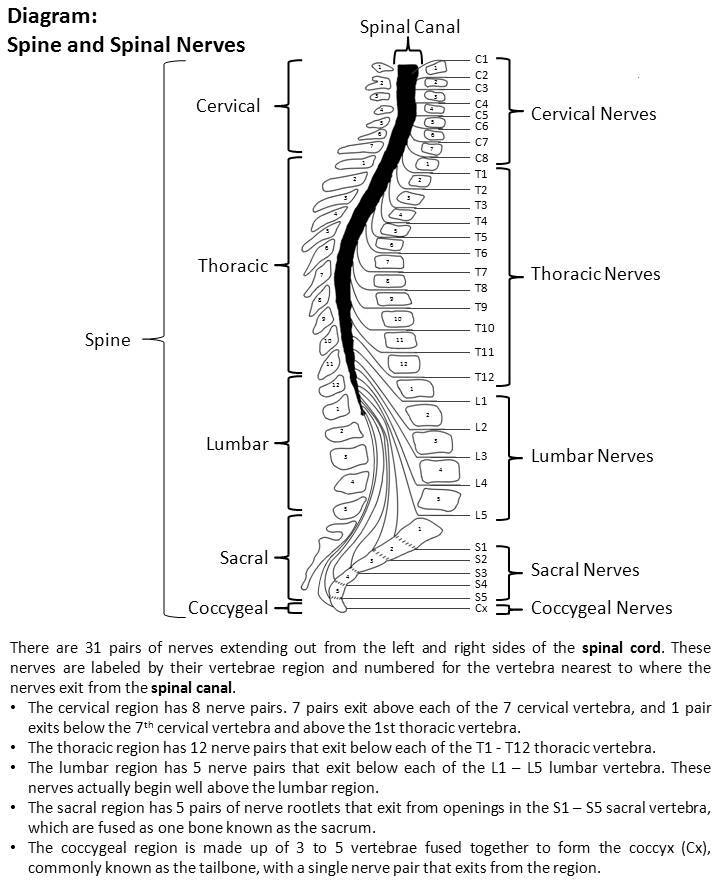
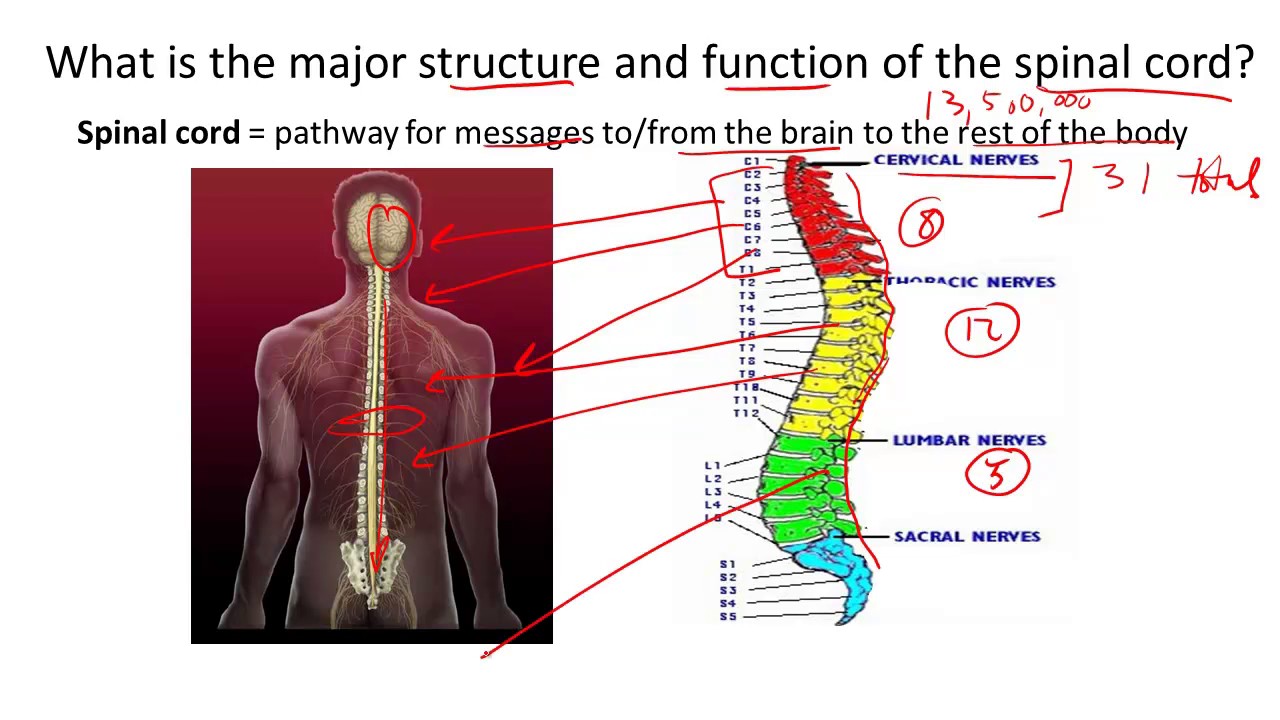
Most vertebrae move to allow for a range of motion. Consists of 31 spinal levels 31 pairs of spinal nerves-- 8 cervical 12 thoracic 5 paired lumbar 5 paired sacral 1 paired coccygeal. The posterior most region of spinal cord tapers into a thin fibrous thread like structure called filum terminale.
There are 8 pairs of cervical 12 thoracic 5 lumbar 5 sacral and 1 coccygeal pair of spinal nerves a total. It extends from the lower end of medulla oblongata to the first lumbar vertebra. In an adult the spinal cord is from 42 to 45 centimeters long.
The spinal cord is a cylindrical cord-like structure that lies in the neural canal of the vertebral column. It extends downwards from the brain stem to the lumbar region. The spinal cord sits within the vertebral canal and is well protected inside the 3.
Like a brain it is also protected by three meninges cerebrospinal fluid and a cushion of adipose tissue. The spinal cord is a long bundle of nerves and cells that extends from the lower portion of the brain to the lower back. Ad Over 27000 video lessons and other resources youre guaranteed to find what you need.
It is segmented with a pair of roots dorsal and ventral roots consisting of nerve fibres joining to form the spinal nerves. The spinal cord extends from the medulla oblongata. The spine has 33 stacked vertebrae small bones that form the spinal canal.
Transverse width of the spinal cord varies. It is a long pipe-like structure arising from the medulla oblongata part of the brain consisting of a collection of nerve fibres running through the vertebral column of the backbone. It is also covered by meninges.
The arrangement of gray and white matterin the spinal cordis relativelysimple. After L1 is the lumbar cistern aka cauda equina dorsal and ventral nerve roots. The lowest vertebrae sacrum and coccyx are fused together and dont move.
The Internal Anatomy of the Spinal Cord. It is covered by the three membranes of the CNS ie the dura mater arachnoid and the innermost pia mater. The spinal canal is a tunnel that houses the spinal cord and nerves protecting them from injury.
Spinal Cord Anatomy Structure Function and Spinal Cord Nerves. The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system CNS that extends from the brain stem to the lumbar region and is contained within the vertebral column. Spinal cord is a cylindrical structure lying in the neural canal of the vertebral column.
Cervical thoracic lumbar sacral and coccygeal. Spinal cord is attached to the coccyx by the terminal filum. The spinal cord is one of the most important structures in the human body.
Each segment of the spinal cord provides several pairs of spinal nerves which exit from vertebral canal through the intervertebral foramina. Watch complete video answer for Describe the structure of spinal cord. It carries signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
It is elongated cylindrical suspended in the vertebral canal and protected by vertebrae Surrounded by the meninges and cerebrospinal fluid CSF. It extends from the lower end of the medulla oblongata to the first lumbar vertebra. View Answer Bookmark Now.
The spinal cord is a complex cylinder of nerves that starts at the base of your brain and runs down the vertebral canal to the backbone. It is part of the bodys collection of nerves called the central nervous system along with the brain. The primary function of spinal cord is a transmission of.
It is continuous to the level of the second lumbar vertebra. The spinal cord is a long thin tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the medulla oblongata of the brain to the level of the lumbar region. Briefly describe the structure of the cerebellum in human brain and mention its functions.
The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system CNS. Structure of Spinal Cord extends from foramen magnum to L1-L2 vertebrae.

Spinal Cord Structure And Functions Definition Examples Diagrams
What Does The Spinal Cord Do Spinal Cord Injury Model System Uab
Describe The Structure Of Spinal Cord Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
No comments for "Describe the Structure of the Spinal Cord."
Post a Comment